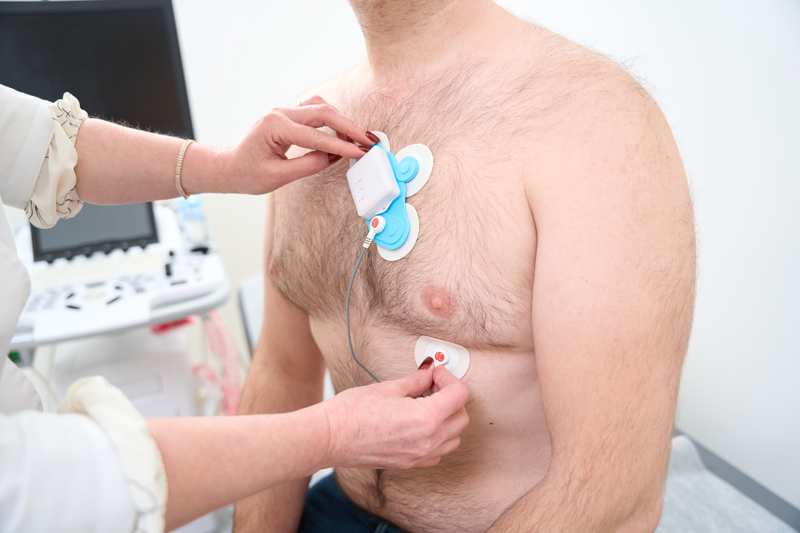
For ECG Holter monitoring to be effective, patient compliance is essential. Traditional Holter monitors, often cumbersome and inconvenient, have been a barrier to long-term monitoring. However, recent innovations in wearable Holter technology have significantly improved patient adherence by offering lightweight, wireless options.
A study in The British Journal of Cardiology found that patient adherence to 48-hour Holter monitoring increased by 27% when using patch-based devices compared to conventional wired monitors. Participants reported improved comfort, ease of use, and less interference with daily activities, which contributed to better-quality ECG recordings and more accurate arrhythmia detection. Additionally, the study highlighted that patients who experienced discomfort or difficulties with traditional Holter monitors were less likely to complete the recommended monitoring period, leading to insufficient data collection and potentially missed diagnoses.
Wireless Holter monitors, now widely available across European healthcare systems, reduce the discomfort associated with traditional devices. These monitors enable extended recording durations, allowing for the detection of infrequent arrhythmias that could be missed with standard ECGs. The NHS and European cardiology clinics are increasingly offering these advanced monitors as part of routine arrhythmia assessments. Extended monitoring capabilities, particularly those exceeding 72 hours, have led to improved detection of intermittent arrhythmias, particularly atrial fibrillation.
Moreover, digital health solutions, including smartphone-linked Holter monitors, have empowered patients to take an active role in their heart health. With real-time data transmission, patients can engage in remote consultations, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits. AI-powered analysis has further streamlined ECG interpretation, enabling faster detection of clinically significant arrhythmias. These innovations also reduce the burden on healthcare providers, as automatic analysis can flag abnormalities, allowing for quicker medical review and intervention.
As wearable Holter technology continues to evolve, patient compliance and diagnostic accuracy are expected to improve, making long-term ECG monitoring a more patient-friendly process. Increased awareness about the benefits of continuous monitoring, along with enhanced comfort and accessibility, will likely lead to greater adoption of these technologies, further improving arrhythmia detection and management.
Reference: Clark, T., Dyer, A., & Watson, K. (2023). Patient-centered ECG Holter monitoring: Advancements in wearable technology. The British Journal of Cardiology, 30(5), 612-622. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjcard/ehb034